Electronic payment methods
The increasingly digitalised and real-time economy is also influencing developments in the way that payments are made. The range of payment applications has expanded substantially in recent years. Even in new payment innovations, however, payments are still largely based on the use of conventional electronic payment instruments. Credit transfer and card payment are the preferred electronic payment instruments in Finland. Data on the use of different payment instruments is available in the Bank of Finland’s payment statistics.

Payment instruments
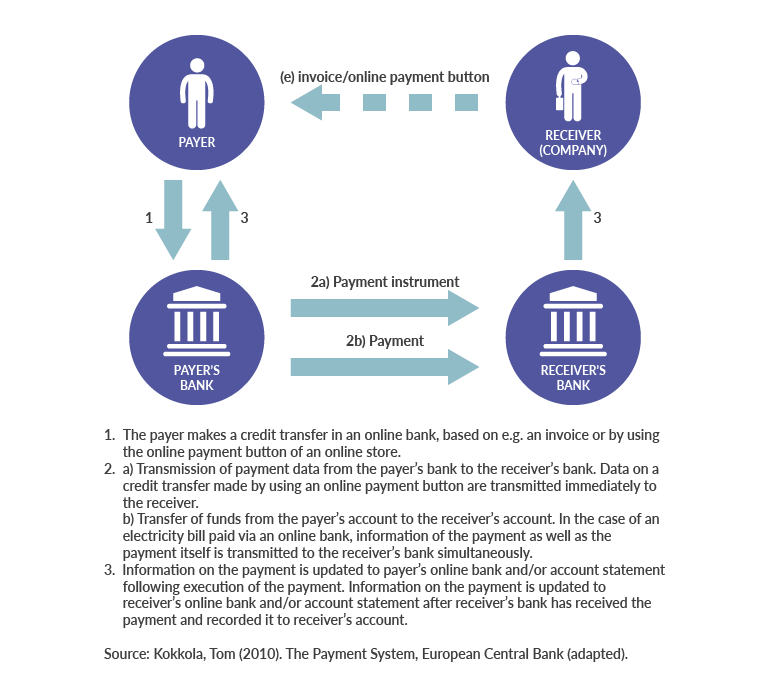
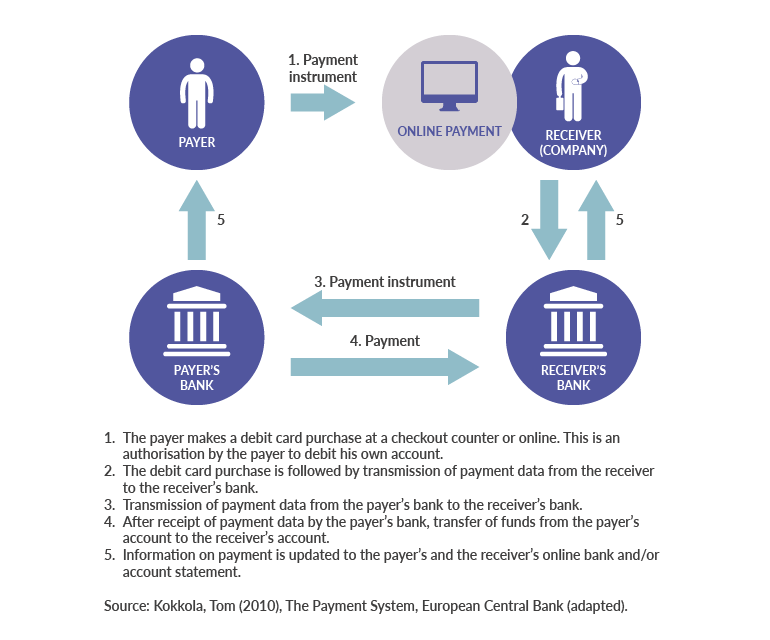
Payment instruments differ from each other in terms of operating principles and are mainly either credit-based or debit-based. In the case of a credit-based payment instrument, the payer initiates the payment transaction by, for example, making a credit transfer in his or her online bank for the payment an electricity bill. In the case of a debit-based payment instrument, the payment transaction is initiated by the payee. In card payments, the card details entered for a purchase in an online shop, for example, authorise the payee’s bank to forward to the payer’s bank a request to debit the account.
Credit-based payment instrument, e.g. credit transfer
Debit-based payment instrument, e.g. payment card
Finland is part of the Single Euro Payments Area (SEPA). In SEPA, there is no distinction between cross-border and domestic payments, and these payments are subject to the same technical and business requirements.
After receiving a payment order, banks have several ways of transferring the payment from the payer’s bank to the payee’s bank. If the payer’s and the payee’s accounts are with the same bank, the payment is transferred as an internal on-us transaction. If the payer’s and the payee’s accounts are with different banks, the payment is transferred either through the correspondent banking network or via payment systems.
In correspondent banking, payments are executed mostly based on banks’ bilateral agreements and arrangements, via the accounts of these banks. This is the procedure applied in payments to payees that are outside the euro area. However, the majority of electronic payments between banks within the euro area are nowadays transferred via payment systems, where the final settlement takes place in central bank money, between the banks’ accounts held with the central bank.